Facebook is a monopoly. Right?
Mark Zuckerberg appeared on national TV today to make a “special announcement.” The timing could not be more curious: Today is the day Lina Khan’s FTC refiled its case to dismantle Facebook’s monopoly.
To the average person, Facebook’s monopoly seems obvious. “After all,” as James E. Boasberg of the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia put it in his recent decision, “No one who hears the title of the 2010 film ‘The Social Network’ wonders which company it is about.” But obviousness is not an antitrust standard. Monopoly has a clear legal meaning, and thus far Lina Khan’s FTC has failed to meet it. Today’s refiling is much more substantive than the FTC’s first foray. But it’s still lacking some critical arguments. Here are some ideas from the front lines.
To the average person, Facebook’s monopoly seems obvious. But obviousness is not an antitrust standard.
First, the FTC must define the market correctly: personal social networking, which includes messaging. Second, the FTC must establish that Facebook controls over 60% of the market — the correct metric to establish this is revenue.
Though consumer harm is a well-known test of monopoly determination, our courts do not require the FTC to prove that Facebook harms consumers to win the case. As an alternative pleading, though, the government can present a compelling case that Facebook harms consumers by suppressing wages in the creator economy. If the creator economy is real, then the value of ads on Facebook’s services is generated through the fruits of creators’ labor; no one would watch the ads before videos or in between posts if the user-generated content was not there. Facebook has harmed consumers by suppressing creator wages.
A note: This is the first of a series on the Facebook monopoly. I am inspired by Cloudflare’s recent post explaining the impact of Amazon’s monopoly in their industry. Perhaps it was a competitive tactic, but I genuinely believe it more a patriotic duty: guideposts for legislators and regulators on a complex issue. My generation has watched with a combination of sadness and trepidation as legislators who barely use email question the leading technologists of our time about products that have long pervaded our lives in ways we don’t yet understand. I, personally, and my company both stand to gain little from this — but as a participant in the latest generation of social media upstarts, and as an American concerned for the future of our democracy, I feel a duty to try.
Facebook is shook, asks for removal of FTC Chair Khan from antitrust cases against it
The problem
According to the court, the FTC must meet a two-part test: First, the FTC must define the market in which Facebook has monopoly power, established by the D.C. Circuit in Neumann v. Reinforced Earth Co. (1986). This is the market for personal social networking services, which includes messaging.
Second, the FTC must establish that Facebook controls a dominant share of that market, which courts have defined as 60% or above, established by the 3rd U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals in FTC v. AbbVie (2020). The right metric for this market share analysis is unequivocally revenue — daily active users (DAU) x average revenue per user (ARPU). And Facebook controls over 90%.
The answer to the FTC’s problem is hiding in plain sight: Snapchat’s investor presentations:
Snapchat July 2021 investor presentation: Significant DAU and ARPU Opportunity. Image Credits: Snapchat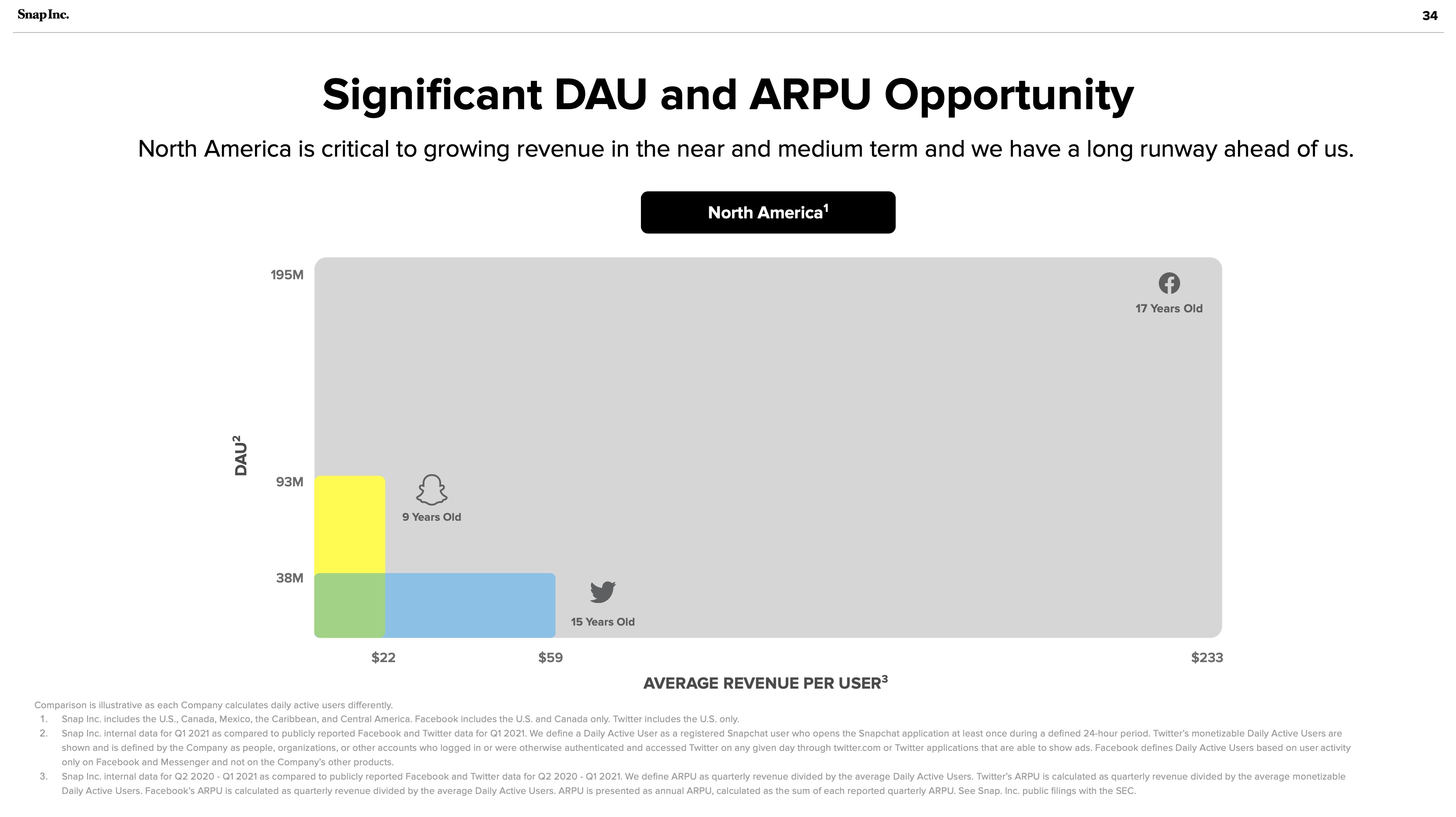
This is a chart of Facebook’s monopoly — 91% of the personal social networking market. The gray blob looks awfully like a vast oil deposit, successfully drilled by Facebook’s Standard Oil operations. Snapchat and Twitter are the small wildcatters, nearly irrelevant compared to Facebook’s scale. It should not be lost on any market observers that Facebook once tried to acquire both companies.
The market Includes messagingThe FTC initially claimed that Facebook has a monopoly of the “personal social networking services” market. The complaint excluded “mobile messaging” from Facebook’s market “because [messaging apps] (i) lack a ‘shared social space’ for interaction and (ii) do not employ a social graph to facilitate users’ finding and ‘friending’ other users they may know.”
This is incorrect because messaging is inextricable from Facebook’s power. Facebook demonstrated this with its WhatsApp acquisition, promotion of Messenger and prior attempts to buy Snapchat and Twitter. Any personal social networking service can expand its features — and Facebook’s moat is contingent on its control of messaging.
The more time in an ecosystem the more valuable it becomes. Value in social networks is calculated, depending on whom you ask, algorithmically (Metcalfe’s law) or logarithmically (Zipf’s law). Either way, in social networks, 1+1 is much more than 2.
Social networks become valuable based on the ever-increasing number of nodes, upon which companies can build more features. Zuckerberg coined the “social graph” to describe this relationship. The monopolies of Line, Kakao and WeChat in Japan, Korea and China prove this clearly. They began with messaging and expanded outward to become dominant personal social networking behemoths.
In today’s refiling, the FTC explains that Facebook, Instagram and Snapchat are all personal social networking services built on three key features:
- “First, personal social networking services are built on a social graph that maps the connections between users and their friends, family, and other personal connections.”
- “Second, personal social networking services include features that many users regularly employ to interact with personal connections and share their personal experiences in a shared social space, including in a one-to-many ‘broadcast’ format.”
- “Third, personal social networking services include features that allow users to find and connect with other users, to make it easier for each user to build and expand their set of personal connections.”
Unfortunately, this is only partially right. In social media’s treacherous waters, as the FTC has struggled to articulate, feature sets are routinely copied and cross-promoted. How can we forget Instagram’s copying of Snapchat’s stories? Facebook has ruthlessly copied features from the most successful apps on the market from inception. Its launch of a Clubhouse competitor called Live Audio Rooms is only the most recent example. Twitter and Snapchat are absolutely competitors to Facebook.
Messaging must be included to demonstrate Facebook’s breadth and voracious appetite to copy and destroy. WhatsApp and Messenger have over 2 billion and 1.3 billion users respectively. Given the ease of feature copying, a messaging service of WhatsApp’s scale could become a full-scale social network in a matter of months. This is precisely why Facebook acquired the company. Facebook’s breadth in social media services is remarkable. But the FTC needs to understand that messaging is a part of the market. And this acknowledgement would not hurt their case.
The metric: Revenue shows Facebook’s monopolyBoasberg believes revenue is not an apt metric to calculate personal networking: “The overall revenues earned by PSN services cannot be the right metric for measuring market share here, as those revenues are all earned in a separate market — viz., the market for advertising.” He is confusing business model with market. Not all advertising is cut from the same cloth. In today’s refiling, the FTC correctly identifies “social advertising” as distinct from the “display advertising.”
But it goes off the deep end trying to avoid naming revenue as the distinguishing market share metric. Instead the FTC cites “time spent, daily active users (DAU), and monthly active users (MAU).” In a world where Facebook Blue and Instagram compete only with Snapchat, these metrics might bring Facebook Blue and Instagram combined over the 60% monopoly hurdle. But the FTC does not make a sufficiently convincing market definition argument to justify the choice of these metrics. Facebook should be compared to other personal social networking services such as Discord and Twitter — and their correct inclusion in the market would undermine the FTC’s choice of time spent or DAU/MAU.
Ultimately, cash is king. Revenue is what counts and what the FTC should emphasize. As Snapchat shows above, revenue in the personal social media industry is calculated by ARPU x DAU. The personal social media market is a different market from the entertainment social media market (where Facebook competes with YouTube, TikTok and Pinterest, among others). And this too is a separate market from the display search advertising market (Google). Not all advertising-based consumer technology is built the same. Again, advertising is a business model, not a market.
In the media world, for example, Netflix’s subscription revenue clearly competes in the same market as CBS’ advertising model. News Corp.’s acquisition of Facebook’s early competitor MySpace spoke volumes on the internet’s potential to disrupt and destroy traditional media advertising markets. Snapchat has chosen to pursue advertising, but incipient competitors like Discord are successfully growing using subscriptions. But their market share remains a pittance compared to Facebook.
An alternative pleading: Facebook’s market power suppresses wages in the creator economyThe FTC has correctly argued for the smallest possible market for their monopoly definition. Personal social networking, of which Facebook controls at least 80%, should not (in their strongest argument) include entertainment. This is the narrowest argument to make with the highest chance of success.
But they could choose to make a broader argument in the alternative, one that takes a bigger swing. As Lina Khan famously noted about Amazon in her 2017 note that began the New Brandeis movement, the traditional economic consumer harm test does not adequately address the harms posed by Big Tech. The harms are too abstract. As White House advisor Tim Wu argues in “The Curse of Bigness,” and Judge Boasberg acknowledges in his opinion, antitrust law does not hinge solely upon price effects. Facebook can be broken up without proving the negative impact of price effects.
However, Facebook has hurt consumers. Consumers are the workers whose labor constitutes Facebook’s value, and they’ve been underpaid. If you define personal networking to include entertainment, then YouTube is an instructive example. On both YouTube and Facebook properties, influencers can capture value by charging brands directly. That’s not what we’re talking about here; what matters is the percent of advertising revenue that is paid out to creators.
YouTube’s traditional percentage is 55%. YouTube announced it has paid $30 billion to creators and rights holders over the last three years. Let’s conservatively say that half of the money goes to rights holders; that means creators on average have earned $15 billion, which would mean $5 billion annually, a meaningful slice of YouTube’s $46 billion in revenue over that time. So in other words, YouTube paid creators a third of its revenue (this admittedly ignores YouTube’s non-advertising revenue).
Facebook, by comparison, announced just weeks ago a paltry $1 billion program over a year and change. Sure, creators may make some money from interstitial ads, but Facebook does not announce the percentage of revenue they hand to creators because it would be insulting. Over the equivalent three-year period of YouTube’s declaration, Facebook has generated $210 billion in revenue. one-third of this revenue paid to creators would represent $70 billion, or $23 billion a year.
Why hasn’t Facebook paid creators before? Because it hasn’t needed to do so. Facebook’s social graph is so large that creators must post there anyway — the scale afforded by success on Facebook Blue and Instagram allows creators to monetize through directly selling to brands. Facebooks ads have value because of creators’ labor; if the users did not generate content, the social graph would not exist. Creators deserve more than the scraps they generate on their own. Facebook suppresses creators’ wages because it can. This is what monopolies do.
Facebook’s Standard Oil ethosFacebook has long been the Standard Oil of social media, using its core monopoly to begin its march upstream and down. Zuckerberg announced in July and renewed his focus today on the metaverse, a market Roblox has pioneered. After achieving a monopoly in personal social media and competing ably in entertainment social media and virtual reality, Facebook’s drilling continues. Yes, Facebook may be free, but its monopoly harms Americans by stifling creator wages. The antitrust laws dictate that consumer harm is not a necessary condition for proving a monopoly under the Sherman Act; monopolies in and of themselves are illegal. By refiling the correct market definition and marketshare, the FTC stands more than a chance. It should win.
A prior version of this article originally appeared on Substack.

