Astroscale hit a major milestone Wednesday, when its space junk removal demo satellite that’s currently in orbit successfully captured and released a client spacecraft using a magnetic system.
The End-of-Life Services by Astroscale-demonstration (ELSA-d) mission was launched in March, with the goal of validating the company’s orbital debris removal tech. The demonstrator package, which was sent up on a Soyuz rocket that launched from Kazakhstan, included two separate spacecraft: a “servicer” which was designed to remove space junk, and a “client” that poses as said space junk.
Astroscale launches its ELSA-d orbital debris removal satellite
“A major challenge of debris removal, and on-orbit servicing in general, is docking with or capturing a client object; this test demonstration served as a successful validation of ELSA-d’s ability to dock with a client, such as a defunct satellite,” the company explained.
The demonstration today showed that the servicer – a model of Astroscale’s future product – can successfully magnetically capture and release other spacecraft.
But that’s not the end for the ELSA-d demonstration mission; the servicer and client still must hit three more capture-and-release milestones before Astroscale can call it a complete success. Next up, the servicer must safely release the client and re-capture it from a greater distance away. After that, Astroscale will attempt the same release-and-capture process, but this time with the client satellite simulating an uncontrolled, tumbling space object. The final capture demonstration the company is calling “diagnosis and client search,” in which the servicer will inspect the client from a close distance, move away, then approach and re-capture.
Image Credits: Astroscale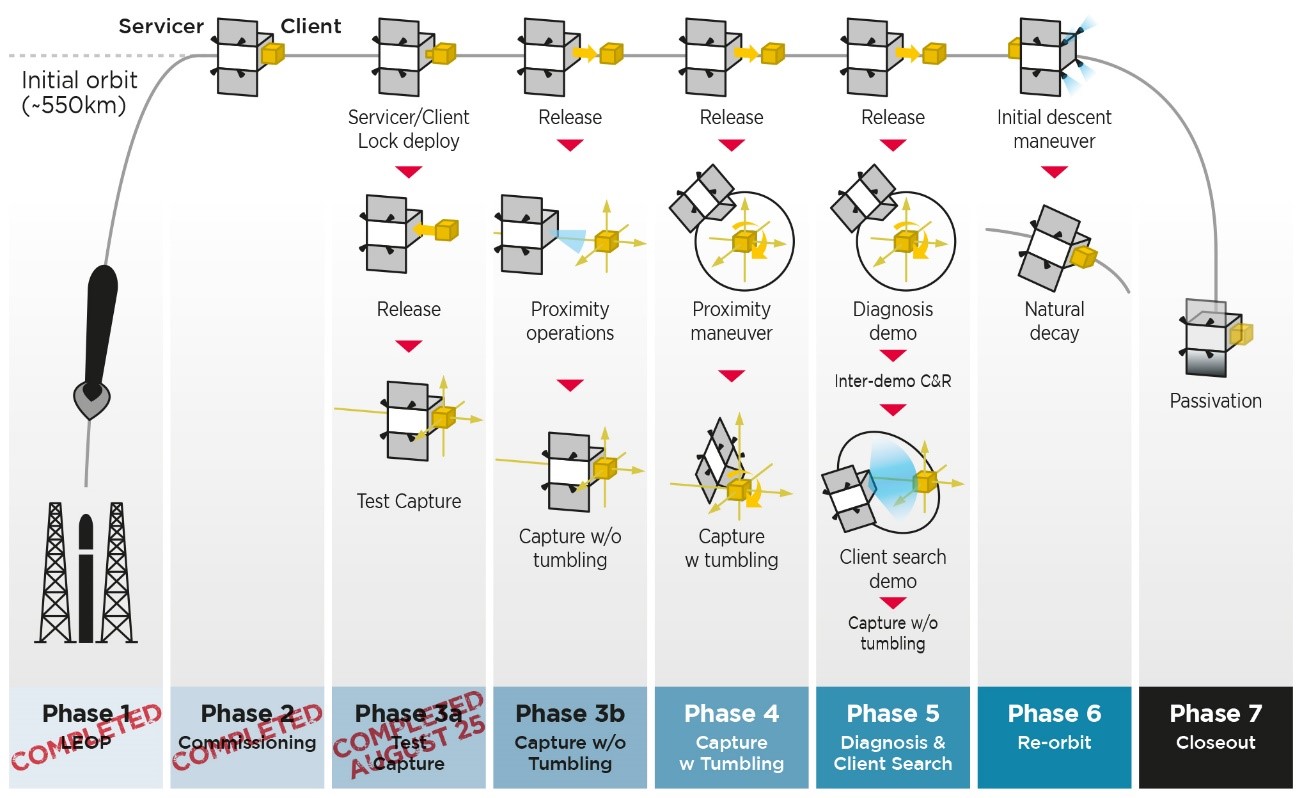
Astroscale is one of a suite of companies working on the problem of orbital debris, but it’s the first to send up a debris removal demonstration mission. According to NASA, over 27,000 pieces of orbital debris are tracked by the Department of Defense’s global Space Surveillance Network sensors. The amount of junk in space is only anticipated to grow as the cost of launching a spacecraft, and other expenses, continue to decline.
You can watch a video of the mission operations team explain the test demonstration here: