Emotional intelligence (also known as EQ or EI) is underneath every choice. Since emotions are forces that influence our daily thoughts and decisions, EQ basically defines how we manage life in general.
The concept first appeared in research by Peter Salovey and John Mayer, but it became widely known through Daniel Goleman’s work in the 1990s. Goleman identified five core components of emotional intelligence that shape how we handle stress, build relationships, and make decisions. These skills are now used in education, workplaces, and leadership development worldwide.
In this article, we’ll explore the 5 components of emotional intelligence, why they matter, and how to strengthen them.
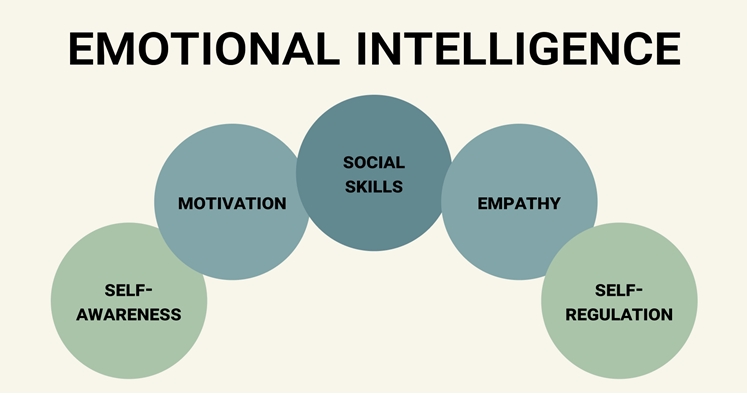
5 Components of Emotional Intelligence Broken Down
According to Daniel Goleman, the5 components of emotional intelligenceare:
- Self-awareness
- Self-regulation
- Motivation
- Empathy
- Social skills
Goleman and the following EQ theorists have chosen these components to describe our interactions with emotions comprehensively. Modern measuring systems like self-reports, performance-based tasks, or the Breeze EQ test apply the same reasoning. They use the five EQ components to assess emotions across different life domains, so as not to miss any growth opportunity.
These skills can be observed daily and, importantly, strengthened with practice. Although some believe that our emotional skills are innate, scientists, and Goleman specifically, were reassured that EQ is fluid and certain practices can improve EQ levels.
Self-Awareness
Self-awareness is the ability to identify and understand your emotions and how they affect your actions. Goleman considered it the cornerstone of emotional intelligence because without self-awareness, the other components cannot develop fully. How can you read the book without knowing the alphabet?
- Why Self-Awareness Is Important
Research from the book Innovation and Capacity Building found that high self-awareness strongly correlates with better decision-making and reduced stress. People who can differentiate between “anxiety” and “irritation,” for example, are less likely to let emotions cloud judgment. Moreover, being aware of how different circumstances and biases (for example, confirmation bias) influence one's decision-making makes a person more objective.
- How to Be More Self-Aware
Being self-aware begins with thinking about your thoughts, feelings, or ideas. Doing this intentionally may be challenging, so people start by building an “emotion dictionary” by regularly journaling or even pausing in the middle of daily routines to name their feelings out loud.
Self-Regulation
Self-regulation is the skill of controlling disruptive impulses and adapting to changing circumstances.
- Importance of Self-Regulation
Goleman emphasized its importance because unregulated emotions, like anger, anxiety, or frustration, are among the most considerable challenges to overcome nowadays. Strong feelings might even sabotage relationships and decision-making, but pretending they don't exist is equally unhealthy.
Self-regulation doesn't mean simply "shutting down" emotions and telling yourself to calm down. Self-regulation is built on self-awareness and self-compassion. This study from the Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology researched how self-regulation practices help people who are quitting smoking. The results of the study are astonishing: not only were people who actively practiced self-regulation more successful in quitting smoking, but they also felt more motivated not to relapse.
- How to Regulate Yourself Better
Although different people find different strategies helpful, here's what's effective according to the science:
- If you feel like saying impulsive things, think them instead of saying. Picture it, elaborate in minor detail, but don't say it.
- Practice “micro-pauses” before responding to emotional triggers. For example, take a deep breath.
- Try “if-then plan.” For example, "If I don't smoke now, then I'll reward myself with a take-out dinner."
Motivation
Motivation is one of the 5 components of emotional intelligence that describes the internal drive to pursue goals with persistence and resilience. Unlike external motivators such as salary or recognition, intrinsic motivation fuels consistent effort even in the face of obstacles.
- Importance of Motivation in EQ Framework
For Goleman, motivation was an essential element. It answers the question, "Why do people with the same skillsets, who are self-aware and empathetic, might not achieve the same results?" Motivation explains why some people maintain long-term success despite setbacks.
Motivation shows up in everyday life, too. A student with high EQ reframes studying as an investment in future independence, while an employee sees routine emails as part of strengthening team collaboration. This perspective shift sustains energy even when rewards are delayed.
- How to Improve Motivation
Connecting daily tasks to personal values is the best way to become more driven, even when daily life becomes dull and the long-term rewards seem far behind the horizon. That's why breaking large goals into smaller milestones works. Yes, it reinforces intrinsic motivation, but it also celebrates progress.
Empathy
Empathy is the ability to sense and understand other people’s emotions. It is one of the differences that sets humans apart from other animals. Being able to feel for somebody else is one of our most significant evolutionary advantages.
- Why Empathy Is Important
Social interactions would be shallow and transactional, theorists argue. Among the 5 components of emotional intelligence, empathy is the first step towards understanding other people. According to Goleman, it's the “social glue” of EQ.
- How to Improve Empathy
Empathy is one of the few components of emotional intelligence that can come naturally. Besides the mental health conditions in which empathetic skills can remain underdeveloped, people are born with the ability to be compassionate. However, the current individualistic culture usually rewards a lack of empathy, suppressing these innate feelings.
To improve empathy, develop the habit of “perspective taking.” Instead of immediately disagreeing, try silently completing the phrase: “They may feel this way because…” Even when you don't have a reason, try to come up with one, and you will calm your brain by giving it logical food for thought.
Another way to train empathy is to imagine yourself in other people’s shoes. Of course, you can do this with your friends or family. But even observing strangers, creating stories for them, and seeing yourself in their shoes can boost empathetic skills.
Social Skills
Social skills are the outward application of the other EQ components. They include communication, conflict resolution, persuasion, and collaboration.
- Social Skills' Importance in EQ Framework
Goleman viewed social skills as an outcome of all previous components. Social abilities translate self-awareness, empathy, and regulation into real-world influence. Without them, EQ remains internal rather than impactful.
According to the Pew Research Center, 42% of jobs in 2018 required social skills as the core responsibility. Social skills go beyond customer excellence or service; managerial and teaching skills also belong there.
- How to Improve Social Skills
○ Use people's names when referring to them.
○ Practice constructive feedback with a compulsory highlight of people's strengths.
○ Never avoid tension, standing up for yourself.
○ Ask open-ended questions and show curiosity in people's answers.
Why The 5 Components of Emotional Intelligence Are Important?
The 5 components of emotional intelligence matter because they predict success and well-being across nearly every life domain. Research consistently shows that even the most technically savvy people need higher EQ for long-term achievement.
A large-scale analysis published in Personality and Individual Differences found that high EQ correlates with lower stress, stronger immune functioning, and better workplace performance. For example, one survey of over 500,000 employees revealed that 90% of top performers scored high in emotional intelligence, regardless of role or industry. In relationships, couples with higher empathy and communication (two EQ components) report greater satisfaction and resilience during conflict.
The importance also extends to leadership and health. Teams led by emotionally intelligent managers demonstrate higher productivity and retention, while individuals with strong self-regulation and self-awareness experience fewer symptoms of anxiety and burnout. Even in education, students who receive EQ training show improved academic outcomes and stronger peer connections.
In short, Goleman’s five components of emotional intelligence are measurable, applicable skills. Developing them means cultivating healthier bodies, more meaningful relationships, and stronger communities. EQ explains not just what we achieve but how we thrive in the process.
Media Contact
Company Name: Breeze
Email: Send Email
Country: United States
Website: https://breeze-wellbeing.com/





