800V Charging pile “Charging Basics”
This article mainly talks about some preliminary requirements for 800V charging piles, first let’s take a look at the principle of charging: When the charging tip is connected to the vehicle end, the charging pile will provide (1) low-voltage auxiliary DC power to the vehicle end to activate the built-in BMS (battery management system) of the electric vehicle After activation, (2) connect the car end to the pile end, exchange the basic charging parameters such as the maximum charging demand power of the vehicle end and the maximum output power of the pile end, after the two sides are matched correctly, the BMS (battery management system) of the vehicle end will send power demand information to the ev charging station, and the electric car charging pile will adjust its own output voltage and current according to this information, and officially start charging the vehicle, which is the basic principle of charging connection, and we need to be familiar with it first.
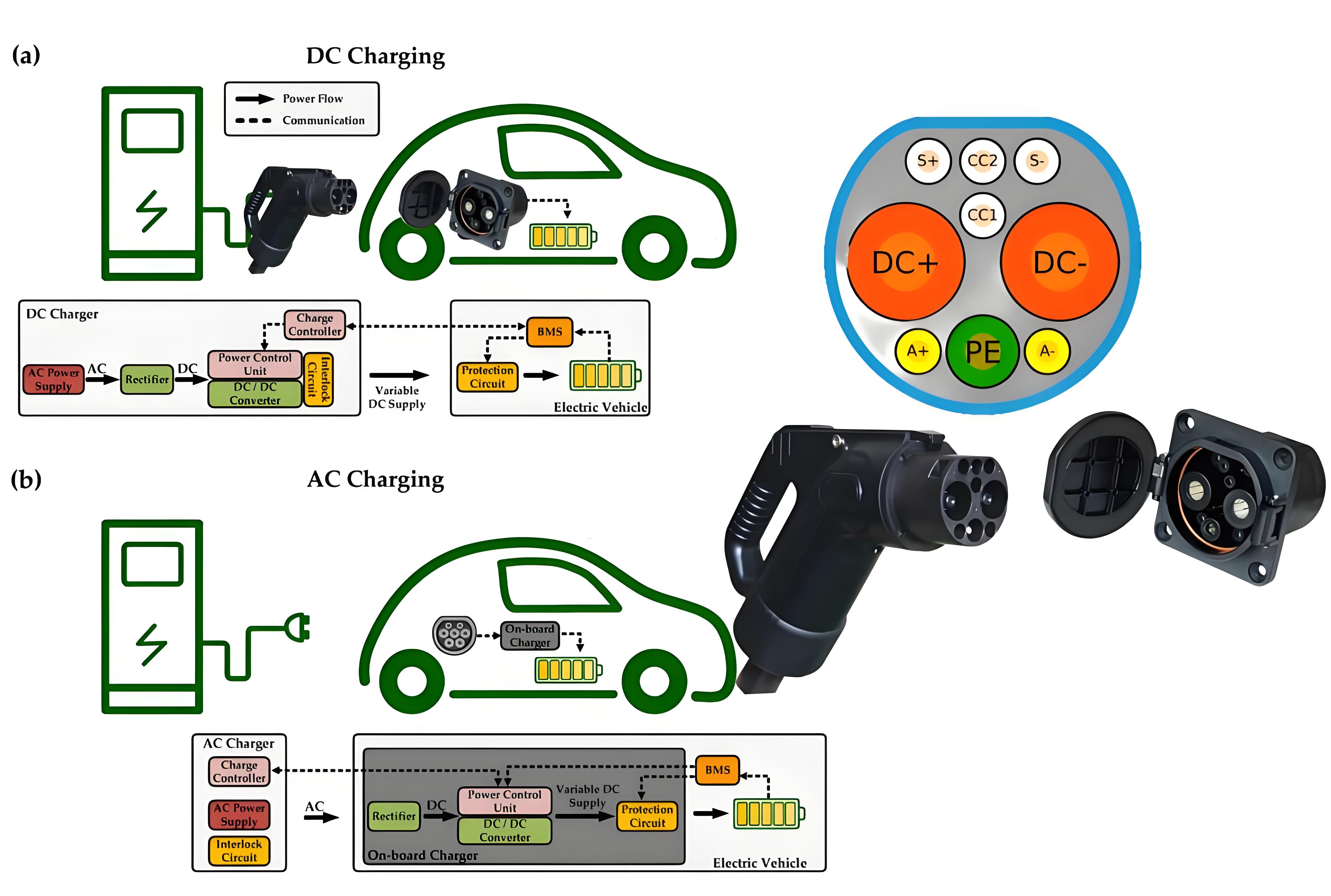
800V charging: “boost voltage or current”
Theoretically, if we want to provide charging power to shorten the charging time, there are usually two ways: either you increase the battery or increase the voltage; According to W=Pt, if the charging power is doubled, the charging time will naturally be halved; According to P=UI, if the voltage or current is doubled, the charging power can be doubled, which has been mentioned repeatedly and is considered common sense.
If the current is larger, there will be two problems, the larger the current, the larger and bulkier the cable that requires current, which will increase the wire diameter and weight, increase the cost, and is not convenient for personnel to operate; In addition, according to Q=I²Rt, if the current is higher, the power loss is larger, and the loss is reflected in the form of heat, which also increases the pressure of thermal management, so there is no doubt that it is not advisable to increase the charging power by continuously increasing the current, whether it is charging or the in-car drive system.

Compared with high-current fast charging, high-voltage fast charging generates less heat and lower loss, and almost mainstream car companies have adopted the route of increasing voltage, in the case of high-voltage fast charging, theoretically the charging time can be shortened by 50%, and the increase in voltage can also easily increase the charging power from 120KW to 480KW.
800V charging: “Thermal effects corresponding to voltage and current”
But whether it is increasing the voltage or increasing the current, first of all, with the increase of your charging power, your heat will appear, but the thermal manifestation of increasing the voltage and increasing the current is different. However, the former is preferable in comparison.
Due to the low resistance encountered by the current when passing through the conductor, the voltage increase method reduces the required cable size, and the heat to be dissipated is less, and while the current is increased, the increase in the current-carrying cross-sectional area leads to a larger outer diameter and a larger cable weight, and the heat will slowly increase with the extension of the charging time, which is more concealed, which is a greater risk to the battery.

800V charging: “Some immediate challenges with charging piles”
800V fast charging also has some different requirements at the pile end:
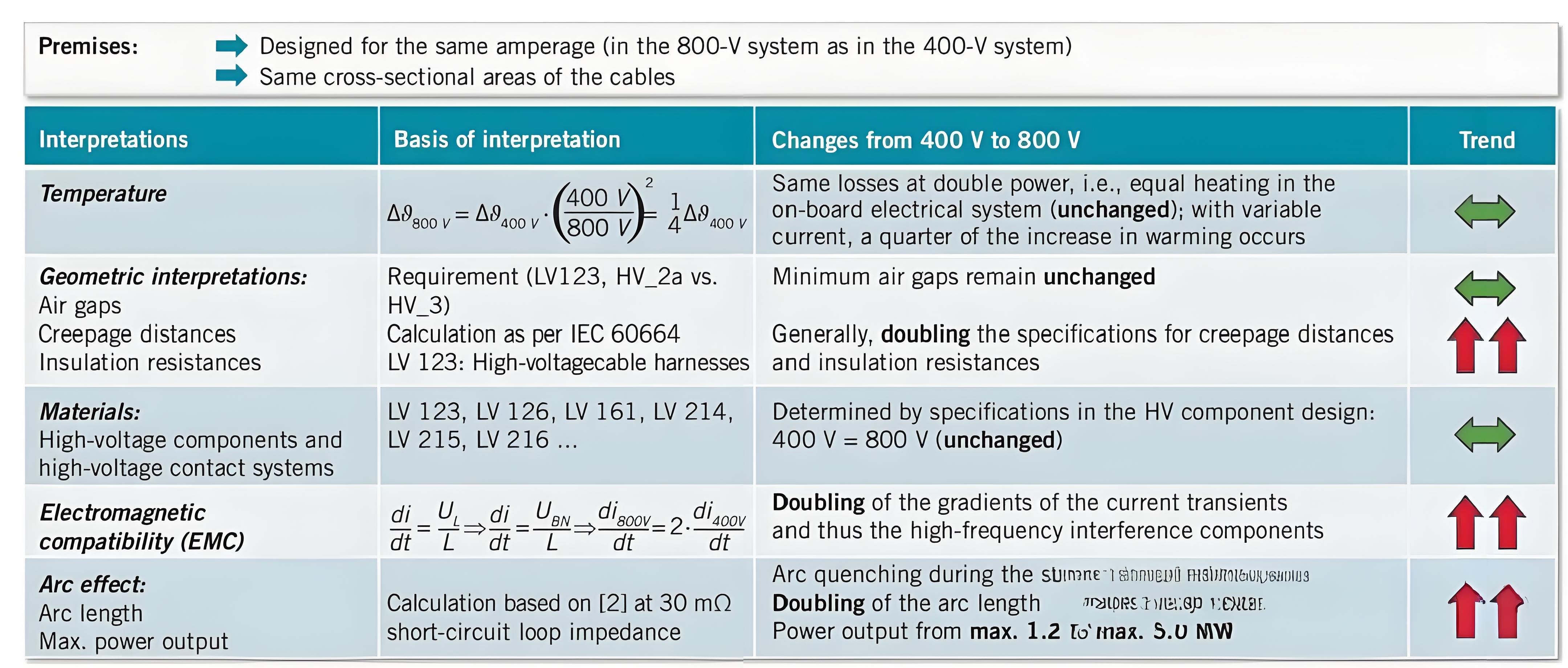
If from a physical point of view, with the increase of voltage, the design size of related devices is bound to increase, for example, according to the pollution level of the IEC60664 is 2 and the distance of the insulation material group is 1, the distance of the high-voltage device needs to be from 2mm to 4mm, and the same insulation resistance requirements will also increase, almost the creepage distance and insulation requirements need to be doubled, which needs to be redesigned in the design compared with the previous voltage system design, including connectors, copper bars, connectors, etc. In addition, the increase in voltage will also lead to higher requirements for arc extinguishing, and it is necessary to increase the requirements for some devices such as fuses, switch boxes, connectors, etc., which are also applicable to the design of the car, which will be mentioned in subsequent articles.
The high-voltage 800V charging system needs to add an external active liquid cooling system as mentioned above, and the traditional air cooling can not meet the requirements whether it is active or passive cooling, and the thermal management of the electric car charging station gun line to the vehicle end is also higher than before, and how to reduce and control the temperature of this part of the system from the device level and the system level is the point to be improved and solved by each company in the future; In addition, this part of the heat is not only the heat brought by overcharging, but also the heat brought by high-frequency power devices, so how to do real-time monitoring and stable, effective and safe to take away the heat is very important, which is not only a breakthrough in materials, but also systematic detection, such as real-time and effective monitoring of charging temperature.
At present, the output voltage of DC charging piles on the market is basically 400V, which cannot directly charge the 800V power battery, so an additional boost DCDC product is needed to raise the 400V voltage to 800V, and then charge the battery, which requires higher power and high-frequency switching, and the module that uses silicon carbide to replace the traditional IGBT is the current mainstream choice, althoughSilicon carbide modules can increase the output power of charging piles and reduce losses, but the cost is also much higher, and the requirements for EMC are also higher.
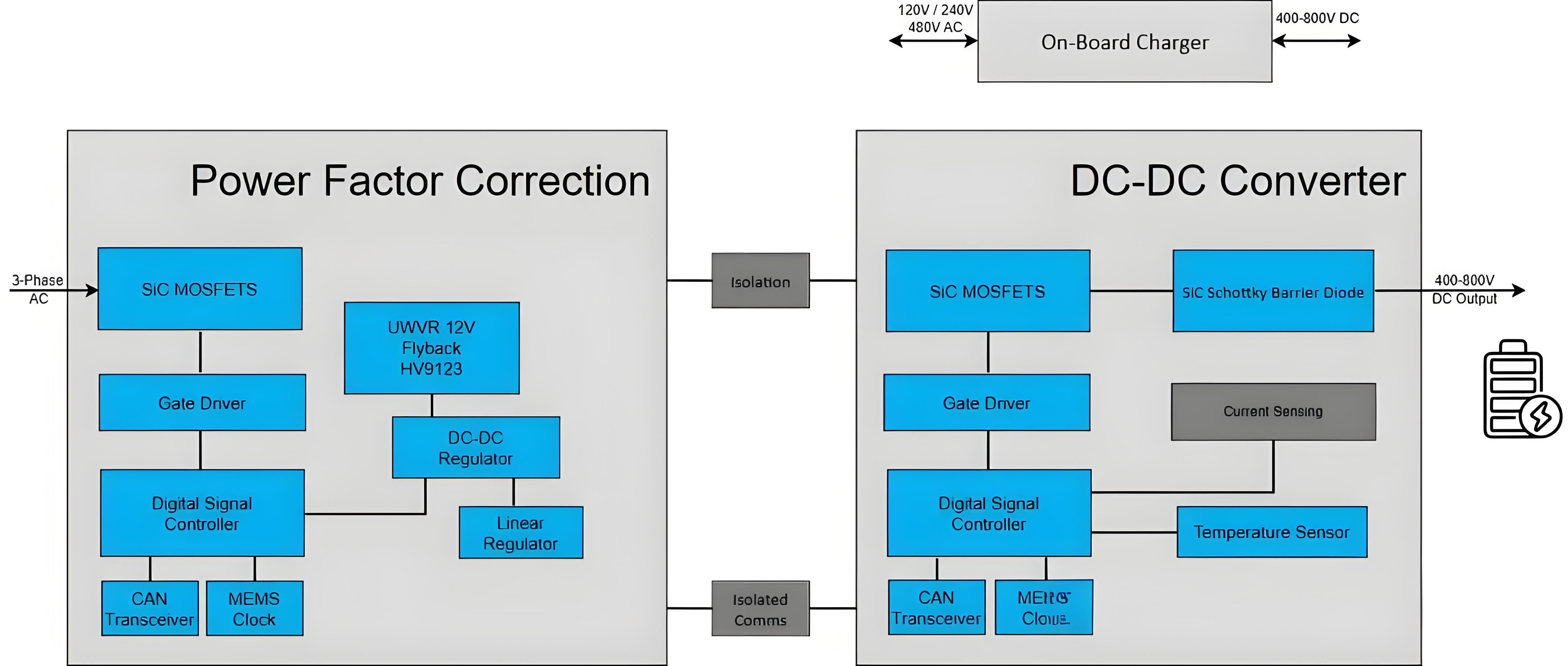
To sum it up. Basically, the increase in voltage will need to be increased at the system level and device level, including thermal management system, charging protection system, etc., and the device level includes the improvement of some magnetic devices and power devices.
Media Contact
Company Name: Beihai Power
Email: Send Email
Country: China
Website: https://www.beihaipower.com/






